2025 Sustainability Audit Report
A Roadmap for Local News Sustainability
Background & Definitions
Definition of Sustainability
LION’s Sustainability Audit is rooted in our three-pillar definition of sustainability, a definition first introduced in 2021 that has been adopted by many industry partners and peers. All three pillars must be strong in order for an organization to be sustainable and stable enough to grow and outlast setbacks.
Operational Resilience
Operational Resilience refers to a news business’s culture, systems, processes and policies designed to support staff/leadership and manage growth. Without robust operational infrastructure, news businesses will experience burnout among those whose talent and buy-in are critical to their success.
Financial Health
Financial Health describes a news business’s plan for earning money, managing a budget, and monitoring revenue and expenses. Without a strong plan and clear policies and processes, news businesses will reach the end of their financial runway without the tools and data they need to grow revenue or right-size their operations.
Journalistic Impact
Journalistic Impact refers to a news business’s track record of producing meaningful and demonstrable impact in their communities and for their audiences. Without a clear plan for reaching audiences and clarity about how to define and measure their impact, news businesses will lose the backing of the investors, sponsors, and audiences whose support fuels their growth.

During the assessment, the Audit uses a range of indicators and metrics to measure development in each of the three pillars.
What’s an Indicator?
A system or practice that illustrates the depth of engagement that an organization has with a given pillar. For example, having an employee handbook is an indicator of Operational Resilience. The analysis looked at nearly 300 indicators — 121 for Operational Resilience, 75 for Financial Health and 101 for Journalistic Impact.
While all indicators contribute to a robust organization, some have a more direct relationship to growth than others. There are 21 key indicators spread across the three sustainability pillars:
Operational Resilience
Financial Health
Journalistic Impact
Has a succession plan in place
Has a budget as part of its financial documents
Engages in regular audience feedback
Has a documented 1 or 3 year plan
Has a balance sheet as part of its financial documents
Defines journalistic impact data
Includes diversity, equity, inclusion, and belonging in its mission
Has an annual budgeting process
Tracks journalistic impact data
Has dedicated revenue staff
Has a bookkeeping process
Uses journalist impact data in workflows
Posts salary rate/ranges when recruiting
Has annual revenue goals
Defines, tracks, and uses journalistic impact data (practices all three activities above)
Ensures compensation is equitable across similar positions within the team
Has a documented process for tracking member/subscriber interactions
Has media liability insurance
Has general liability insurance
Has a payroll system
Offers flexible work hours
Maturity Model
The program analyzed indicator data to place each organization in one of four stages of maturity for the organization as a whole and for each of the three pillars.

Preparation
News businesses in this stage are working to establish foundational infrastructure while identifying effective revenue streams and journalism products for their market. Preparation stage businesses are often driven principally by their founder(s).

Building
News businesses in this stage have established infrastructure but still require development, likely across all three pillars of sustainability. Many businesses in the Building stage are focused on growing their audience and revenue in order to hire staff beyond the founder(s).

Maintaining
News businesses in this stage have an established infrastructure. But they still seek the ability to sustain operations and generate profits consistently over time.

Growing
News businesses in this stage have achieved mission critical operational and financial infrastructure. They have reached a level of viability across the three pillars and are often working to scale or establish clear plans for succession and future stability.
What Comes After Growing?
What is the definition of sustainable for an independent news organization? The data does not lend itself to a definition, but we do have some considerations to contribute to the conversation. A sustainable organization is one that has strong practices of defining, tracking, and strategically using data across all three pillars of sustainability which can allow it to:
- Proactively plan for growth, whether that’s a new product, market, or acquisition
- Weather a founder or leadership transition without a significant hit to operations
- Maintain operations through a hardship that impacts two or more pillars of sustainability at a time

Program Results
Placing news businesses within the maturity model enabled the program to identify the most relevant and actionable steps to help each participant reach the next stage. It also provided a framework for tracking progress.
Making progress
In all, 45 percent of the 98 organizations that received a follow up assessment progressed to the next stage overall, with an additional 32 percent progressing within at least one pillar.
Proportional stage assignment after implementing new activities
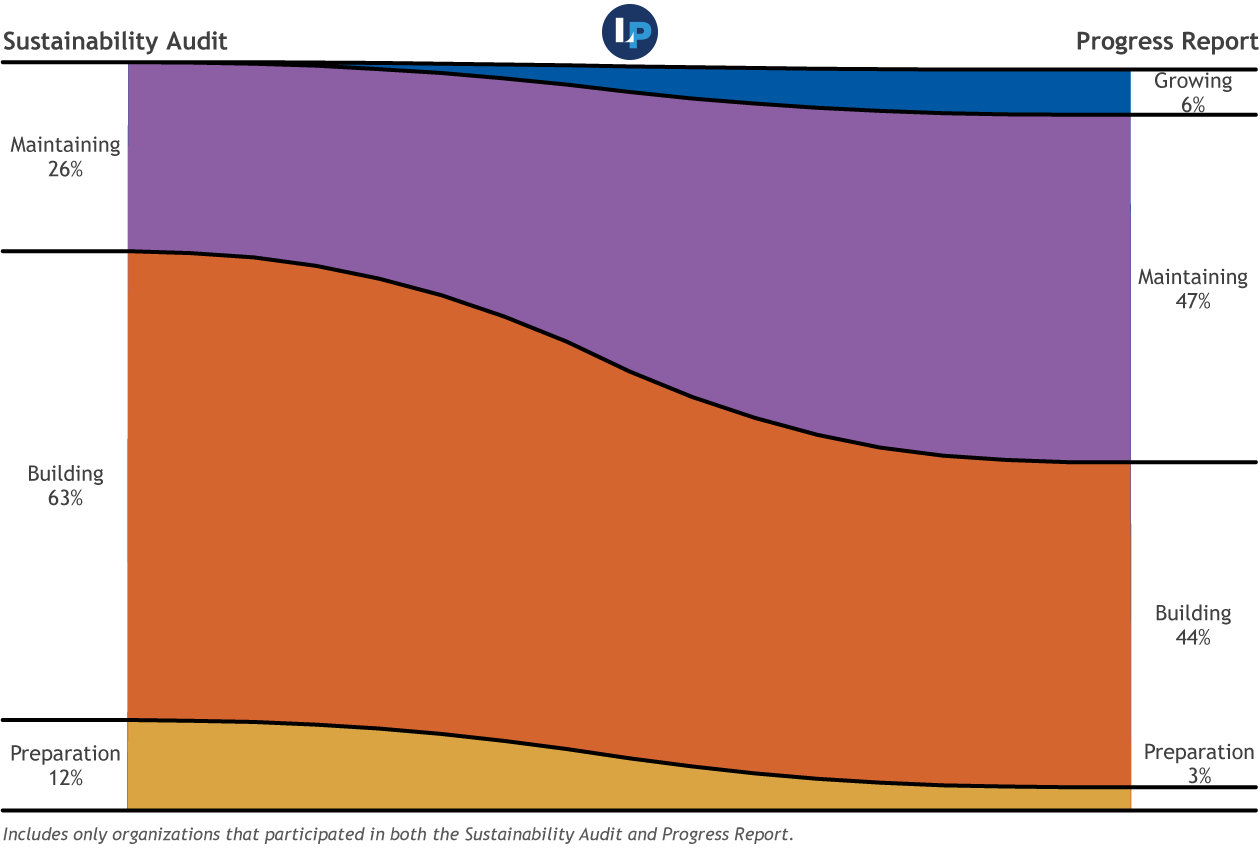
On average, key activities in place grew by 23 percentage points, illustrating that publishers responded to the detailed list of items on which to improve
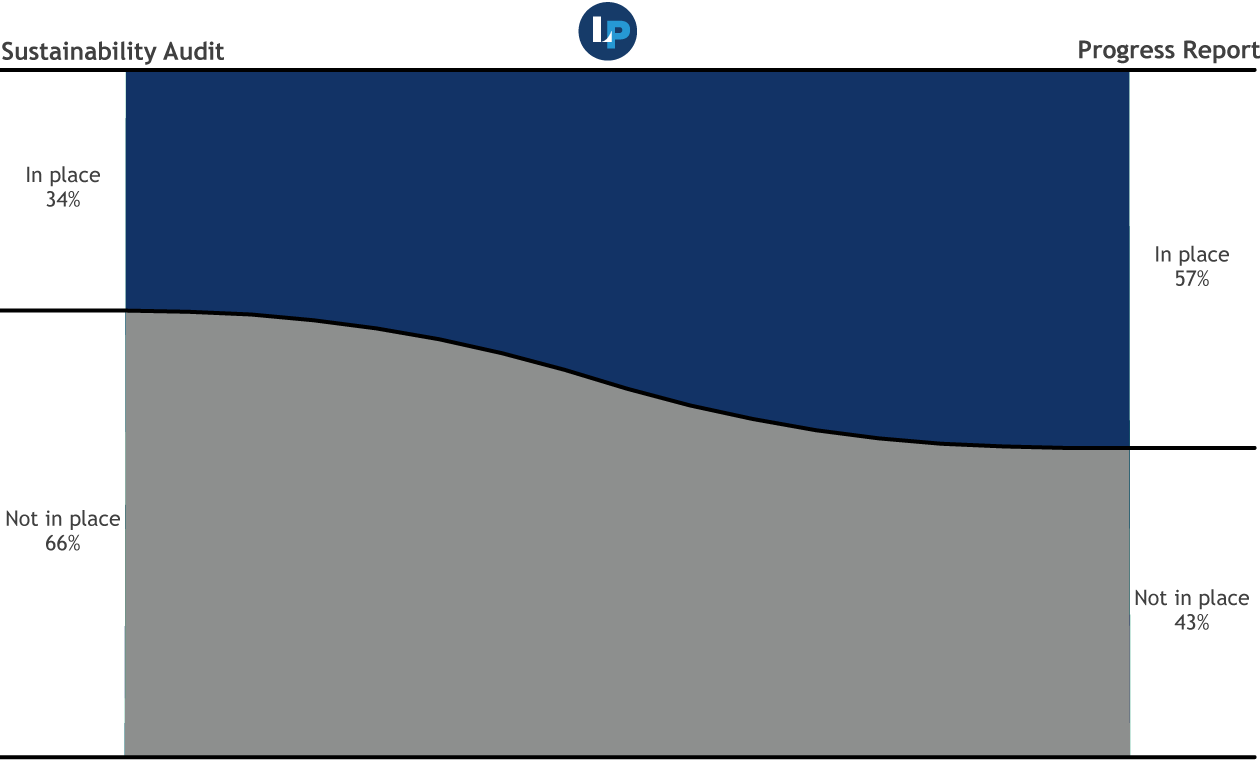
Taking action
When provided with detailed and prioritized items upon which to improve, publishers took action, checking 23 percentage points more key indicators off their to-do lists over the life of the program. On average, a participating organization went from having fewer than one in 10 key indicators in place to implementing nearly six in 10.
Growing revenue
In addition to adoption of new practices, participants also saw revenue growth. A significant majority of organizations that took both the Audit and a follow-up assessment a year or more later saw revenue increases. This suggests that participating organizations made changes that increased their revenue.
Median annual revenue grew by 62% among participating organizations

Areas of focus in funding requests
It’s worth noting that across every stage of organization, assistance with planning and strategy was the most common or second most common use for the funds the program provided to participants.
This suggests that, regardless of what else characterizes an organization, there will always be a need to support organizational strategy and offer direct coaching to newsrooms. Beyond those similarities we see areas of interest that align with expected priorities for each stage:

Preparation
Areas of focus for Preparation organizations are consolidated around revenue-generating activities given that many may need to increase revenue in order to grow staff and product offerings.

Building
While Building organizations still have work to do in building up revenue-generating practices, their primary focus may turn to long-term planning, building infrastructure, and audience. These are activities that cross all three pillars.

Maintaining
“Planning/strategy” was by far the most frequently recommended category, suggesting that while organizations in this stage may have day-to-day operations running smoothly, most need to devote at least some time to strategizing for the future.

Growing
The most frequent categories show that many Growing organizations may revisit Building practices as they expand to new audiences or launch new products.
Frequency of focus areas for organizations in each stage
Funding request focus
Preparation
Building
Maintaining
Growing
Advertising/sponsorships
10
50
29
3
Analytics/metrics
0
20
11
1
Audience growth/marketing
11
62
34
7
Audience research
6
36
26
3
Financial management
9
62
19
3
Grants/philanthropy
5
10
17
0
Individual donors
7
15
12
2
Legal/HR/compliance support
2
23
10
2
Newsletter, website, podcast or other product
5
31
17
1
Planning/strategy
12
63
59
8
Reader revenue/membership programs/subscriptions
15
56
30
7
Staff/freelance compensation
9
58
25
2
Tools/technology
5
18
13
3
Other
1
14
9
1
Who took the Sustainability Audit?
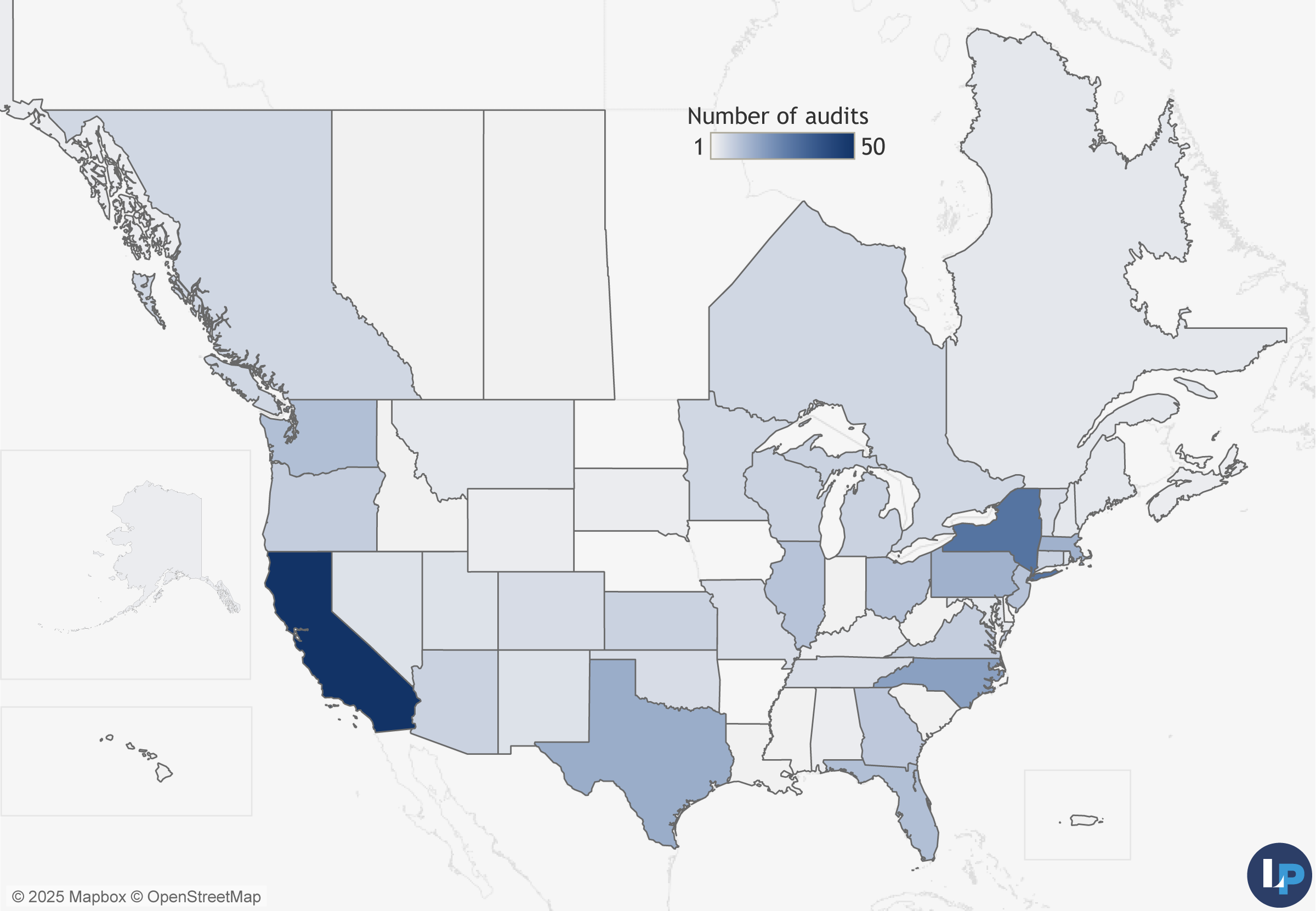
Location
News organizations from 46 states, Puerto Rico, and five Canadian provinces participated in the Sustainability Audit program.
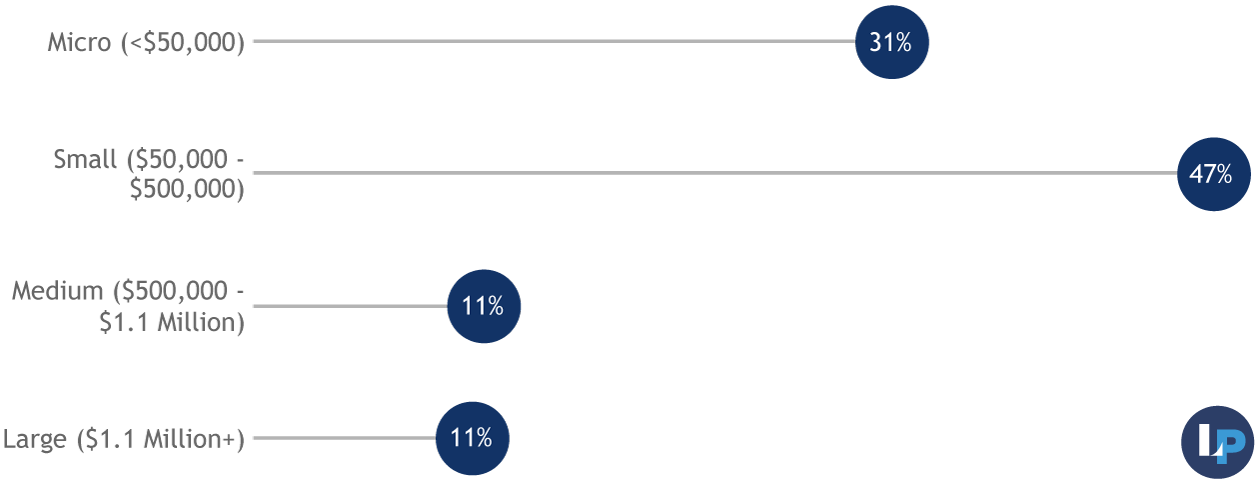
Revenue
Most Audit-takers operate with small budgets — 116 micro and 183 small-budget organizations participated. The median previous year revenue for Audit-takers was $135,989, while the median previous year expenses was $115,000.
Tax Status
Similar to LION's overall membership, the organizations that participated in the Sustainability Audit are closely split between for-profit and not-for-profit: 56 percent of organizations are for-profit, while 44 percent are not-for-profit.

Geographic Scope
Most Audit participants (77 percent) provide local news for cities/towns or counties/regional districts.

Age
More than half (53 percent) of organizations took the audit in their first five years of operation.

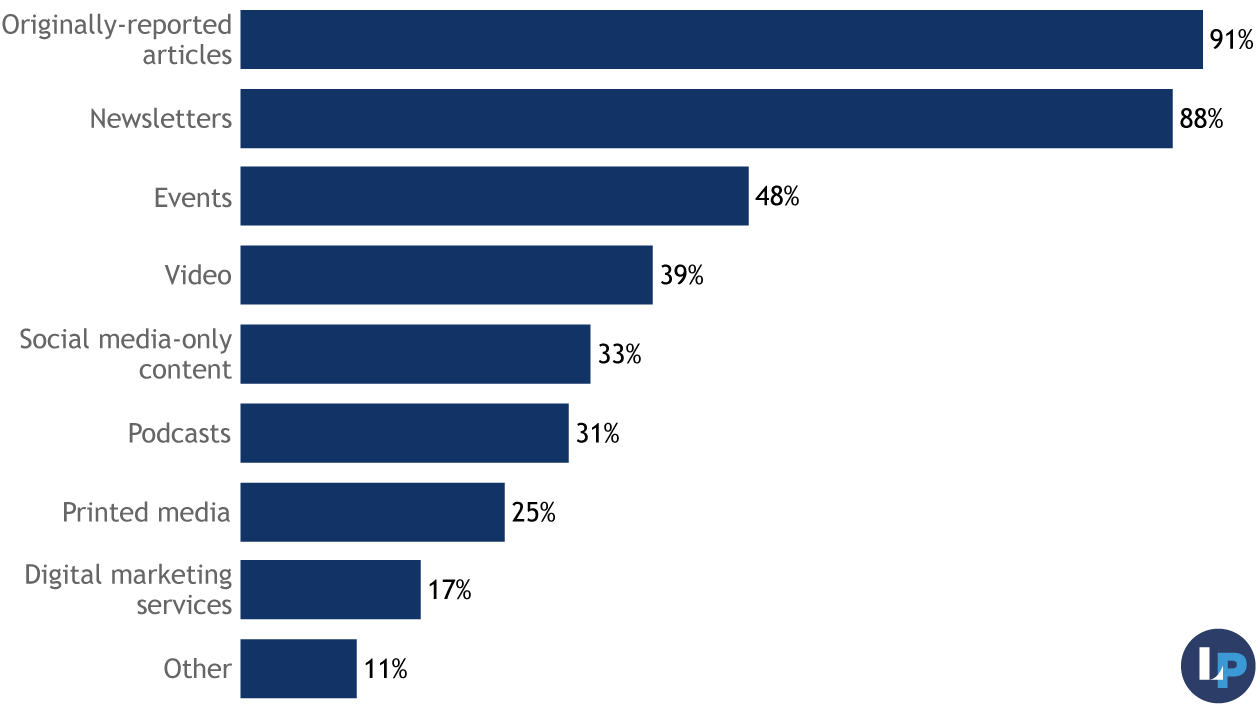
Editorial Strategy and products
As is typical of the field, originally-reported stories and newsletters are the backbone products for most Audit-taking organizations. Smaller numbers reported other products such as events, podcasts, or digital marketing services.
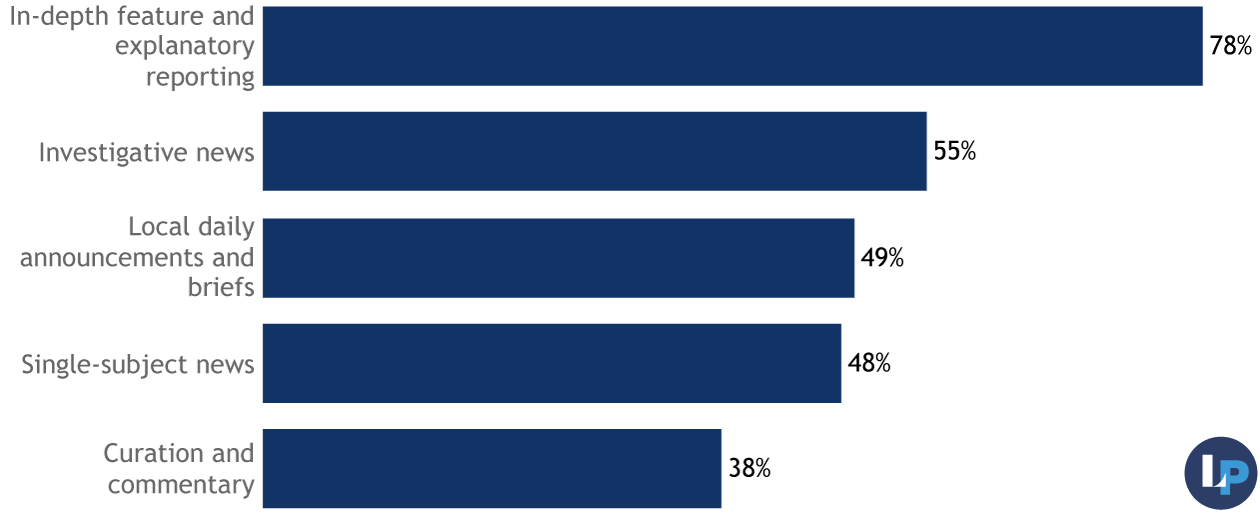
Report Methodology
Our analysis includes data from 357 unique news organizations that participated in a Sustainability Audit between 2022 and 2024 as part of their participation in the Sustainability Audits and Funding program. The dataset includes 459 total records, including both Sustainability Audits and follow up assessments for 98 of the participants. (Moving forward, follow up assessments will be conducted via the new self serve Audit tool available to all LION members.)
While this report relies on data from participating organizations, LION’s membership and Audit participants reflect a wide swath of organizations in the journalism and media sector, and we believe insights from this analysis will help inform the broader field.
Read the full report

Contact
If you’re interested in learning more about the data in this report, please email LION’s Director of Data and Evaluation, Chloe Kizer at chloekizer@lionpublishers.com.
If you’re interested in learning how the LION Sustainability Audit can help the news businesses you work with, please reach out to Andrew Rockway at andrewrockway@lionpublishers.com.
